Common Water Problems, and Solutions
Here are the most common well-water related problems that we are able to correct using household filtration systems.
If you are experiencing any of these, or similar issues, simply contact us for a FREE Water Evaluation & Consultation. We will conduct a thorough test of these parameters, provide the results, and help you find an appropriate treatment solution.
Low pH (Acidic Water)
Excessive acidity in water tends to dissolve piping systems (lead, iron, copper and other metals) , leading to blue/green staining and possible health related problems. Water with a pH parameter less than 6.8 causes significant corrosion of copper piping, and can cause leaks or even breakage over the long-term.
The Solution: Common treatment for acidic water is accomplished by installing a pH Neutralizing system.

PFAS
Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are a family of man-made chemicals related to several consumer products, most notably Teflon, non-stick packaging and fire-fighting foam. PFAS are found in water, and have also been found in human blood around the world due to the ubiquitous use of consumer products that have used the chemicals.
The Solution: Common treatment for PFAS is accomplished by installing a system using Colloidal Activated Carbon.

Sulfides (rotten eggs!)
Hydrogen Sulfide is a gas with a foul rotten egg odor that is very corrosive to most metals. In high concentrations it is flammable and poisonous. It may leave a black slimy substance in pipes and appliances.
The Solution: Reduction of Hydrogen Sulfide in water can be accomplished through oxidation or perpetual sanitation of well water.

Manganese
Manganese is a common mineral found in soil. It can cause black/brown staining, metallic taste and black sediment to form in pipes. When manganese levels exceed the maximum containment level of 0.05 ppm it should be removed.
The Solution: There are a number of filtration systems that can accomplish this. A Water Softener is one.

Iron Bacteria
Iron bacteria live by obtaining energy through the oxidation of ferrous iron to ferric iron and utilize the resulting CO2 to create organic molecules for their existence. Growths of these bacteria result in a gelatinous material, which can clog pipes and cause a foul taste. This material often forms in the tanks of toilets and will produce a "rainbow" slick on the surface.
The Solution: The removal of iron bacteria can be achieved by sanitizing the well system (possibly a perpetual sanitizing system should be considered).

Nitrates
High levels of Nitrates usually indicate intrusion of agricultural fertilizers into the water source. This containment should be treated in levels above 10 ppm. Consumption of this contaminant by infants can cause Methemogloinemia (blue baby disease).
The Solution: A Reverse Osmosis filtration system or Ionic Exchange are both effective ways to remove Nitrates from water.

Hardness
Hardness in water is due to the presence of calcium or magnesium compounds (which exist in all natural water supplies). Hard water is responsible for lime scaling in pipes, water heaters, boilers, humidity, systems, etc. This causes inefficiency and may lead to permanent damage. Acting as an insulator, this scale can seriously reduce the efficiency in water heaters. Hardness also increases soap consumption by wasting up to 90% of the soap (depending on the level of hardness). This results in formation of soap curd, which adheres to clothes, dishes, hair and skin. Soap curd causes poor results in laundering and may hold pathogenic organisms.
The Solution: Reduction of hardness can be achieved by installing a Water Softening System.

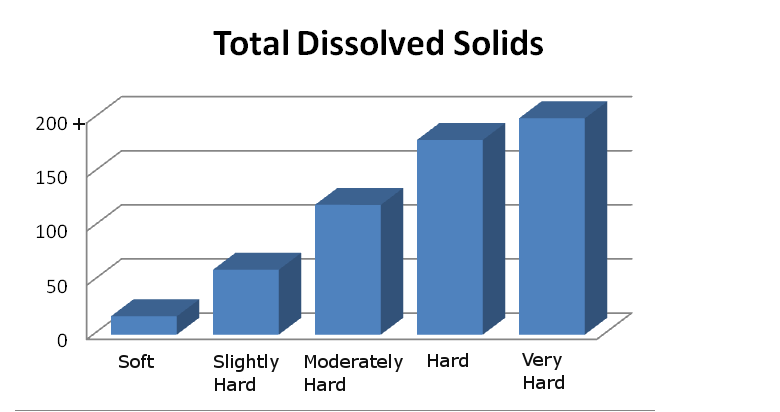
High TDS
Total Dissolved Solids are the sum total of all mineral components dissolved in water. They consist primarily of salts of calcium, magnesium, or sodium (they are usually in the form of chlorides, sulfates or bicarbonates). For household water supplies, especially for drinking, the lower the TDS the better the water quality. Also, an indicator of corrosivity (related to lead levels in the water), can damage plumbing and limit the effectiveness of soaps and detergents.
The Solution: The reduction of TDS is accomplished through a Reverse Osmosis Purification System.
Iron
Iron is a naturally occurring element in soil. From soil it can leach into well water. Iron effects taste and can cause staining (brown, rust) to plumbing fixtures, enamel, kitchenware and clothes. Iron exceeding the maximum contamination level of 0.3 ppm should be removed.
The Solution: Iron problems are handled in various ways, and in accordance to the given situation. Water Softeners & Birm Filters are two common solutions.

Tannins
Tannins come from decaying organic materials (i.e. leaves, vegetation). Its presence can cause taste, odor, and staining.
The Solution: Tannins can be treated with a Water Conditioning system that contains anion resins and catirons. Other methods such as Chlorination or installing Granulated Activated Carbon can also be used.

Copper
Copper is most commonly found in residential water because of the corrosion of copper pipes in the house's plumbing. .
The Solution: Installing a pH Neutralizing system at the point of entry raises the pH value, therefore eliminating corrosive conditions


